Carpal tunnel syndrome is the clinical translation of compression of the median nerve at the wrist. This nerve innervates the hand on the sensory plane (thumb, index, middle and half of the ring finger) and motor (muscles of the base of the thumb).
The nerve and flexor tendons pass through a bony canal (the carpal tunnel) which is covered with a thick ligament (the anterior ring ligament). Any increase in pressure in the carpal tunnel causes nerve pain.
Treatment
Symptoms may decrease with medical treatment. In case of associated pathology (diabetes, hypothyroidism, …), the treatment of the disease usually relieves carpal tunnel syndrome.
The rest of the hand concerned, a correct working position, or even wearing a brace of rest can help reduce the compression of the median nerve.
Intra-ductal infiltration can also relieve symptoms.
If signs persist or worsen, surgical treatment should be used. The purpose of the surgery is to cut the ligament covering the nerve, to reduce the pressure. The consequences are usually simple, the patient can resume a light activity in the week following the intervention. The force recovers in 6 to 12 weeks. Healing of the incision is complete in 15 to 21 days.
The cervical spine (or cervical spine) consists of 7 vertebrae stacked and separated by disks, except between the 1st and 2nd cervical vertebra (C1 and C2).
In the middle of the cervical spine is the spinal canal containing the spinal cord.
The normal intervertebral disk is a flat, cylindrical structure uniting the two vertebrae and acting as a shock absorber.
The disc deterioration is characterized by tears or fissures of the fibrous ring. The causes are dehydration due to aging, microtrauma due to mobility constraints and sometimes also traumas such as cervical sprains.
WHAT ARE THE OBJECTIVES OF SURGERY?
The purpose of the procedure is to remove the herniated disc to release the nerve root (or even the spinal cord) and to remove the pain in the upper limb
This goal is achieved in about 90% of cases. On the other hand, it can persist neck pain
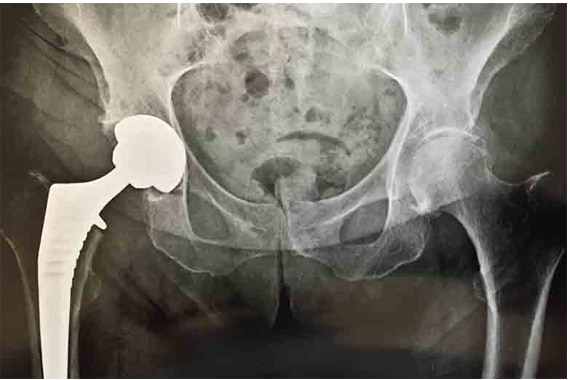
The implementation of a total hip replacement is suggested by the doctor when the disability has become severe and when joint damage is very advanced.
The patient needs to know what the intervention is and how it is exposed in the aftermath.
After being well informed, he decides. “Total” means that the prosthesis concerns the 2 parts of the hip joint: the part of the pelvis (the acetabulum) and the part of the femur (the head).
The models of total prosthesis are not lacking. They vary according to the shape, the material and the method of fixation of the prosthesis.
Pain that has not been sufficiently relieved by antalgic medications and the resulting handicap (walking problems, reduced activity) are good reasons to consider the introduction of a total hip prosthesis.
If, in addition, the osteoarthritis lesions are very advanced on the most recent radiographs, it is an additional reason to think about it.
The lifespan of a prosthesis varies from 15 to 25 years depending on the age, weight and activity of the patient.
Sorry, this entry is only available in French and Arabic.